Kotlin List.slice()
In Kotlin, the slice() function of List class is used to extract sublists from lists based on specified indices. The List slice() function creates a new List containing the sliced sublist.
Syntax
The slice() function takes an IntRange of indices and returns a new list containing elements from the original list at those indices.
fun <T> List<T>.slice(indices: IntRange): List<T>| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| indices | An IntRange specifying the indices of elements to include in the sublist. |
Return Value
The slice() function returns a new list containing elements from the original list at the specified indices.
Example 1: Basic Usage
This example demonstrates how to use slice() to extract a sublist from a list.
In this example,
- Take a list of numbers in the variable numbers.
- Call slice() function on the list numbers and specify the range from 2 to 5.
- The slice() function returns a new list with the elements of numbers from index=2 to index=5 (inclusive).
Kotlin Program
fun main() {
val numbers = listOf(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9)
val sublist = numbers.slice(2..5)
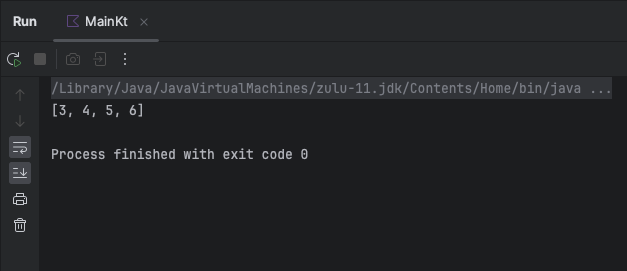
println(sublist) // Output: [3, 4, 5, 6]
}Output
Example 2: Slicing a List of Strings
In this example, we extract specific elements from a list of strings using slice().
In this example,
- Take a list of color strings in the variable colors.
- Call slice() function on the list colors and specify the range from 1 to 3.
- The slice() function returns a new list with the elements of colors from index=1 to index=3 (inclusive).
Kotlin Program
fun main() {
val colors = listOf("Red", "Green", "Blue", "Yellow", "Orange")
val selectedColors = colors.slice(1..3)
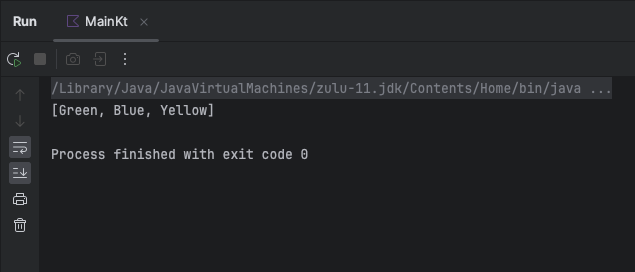
println(selectedColors) // Output: [Green, Blue, Yellow]
}Output
Summary
The slice() function in Kotlin is useful for extracting sublists from lists based on specified indices. We have seen the syntax, and basic usage of the List.slice() function with a couple of examples.