In Kotlin, lambda expressions can have multiple parameters, and you specify them in the lambda’s parameter list before the arrow ->.
Example 1: Lambda function with two parameters
In the following example, we define a lambda function, that takes two parameters, which are integer values, and return their sum.
Kotlin Program
// Lambda Function with two parameters
val sum: (Int, Int) -> Int = { x, y -> x + y }
fun main() {
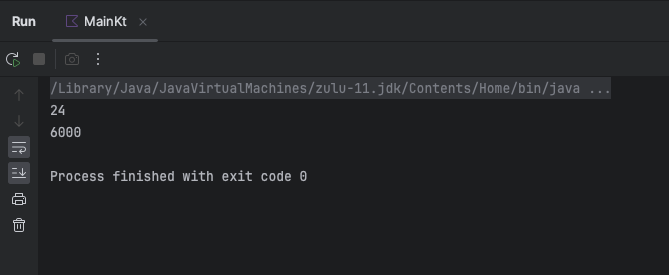
println(sum(5, 10)) //15
println(sum(100, 200)) //300
}The two parameters are received in x, y, before the ->.
Output
Example 2: Lambda function with three parameters
Now, let us take an example, where we define a lambda function that takes three parameters, which are integer values, and return their product.
Kotlin Program
// Lambda function with three parameters
val product: (Int, Int, Int) -> Int = { x, y, z -> x * y * z }
fun main() {
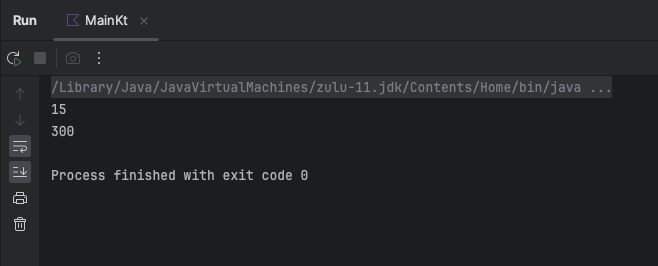
println(product(2, 3, 4)) //24
println(product(10, 20, 30)) //6000
}The three parameters are received in x, y, z, before the ->.
Output